In 2025, artificial intelligence is writing code. AI-powered smart contracts are emerging as developers leverage large language models (LLMs) to generate Solidity and other blockchain code in a fraction of the time. This trend promises to accelerate development, but it also raises a critical question: How can we trust machine-generated on-chain logic? Hidden flaws or exploits could lurk in AI-written code, potentially leading to costly vulnerabilities. This is where AI smart contract audits come into play.
In this article, we’ll explore the rise of AI-generated smart contracts, the unique risks they pose, and how to audit and verify this machine-generated logic. We’ll also look at Twendee’s approach to safeguarding AI-written contracts through a blend of advanced audit automation, logic verification and expert review.
The Rise of AI-Generated Smart Contracts (LLM Code Generation)
Recent advancements in LLM code generation have made it possible to create entire smart contracts from natural language prompts. Developers can ask an AI assistant to “write a smart contract for a token sale” or “create an NFT marketplace contract,” and receive functional code as a starting point. This AI-driven approach lowers the barrier to blockchain development by producing boilerplate code and even complex contract logic within seconds. For busy development teams, the allure is clear: faster delivery, lower cost, and the ability to iterate quickly on decentralized applications.
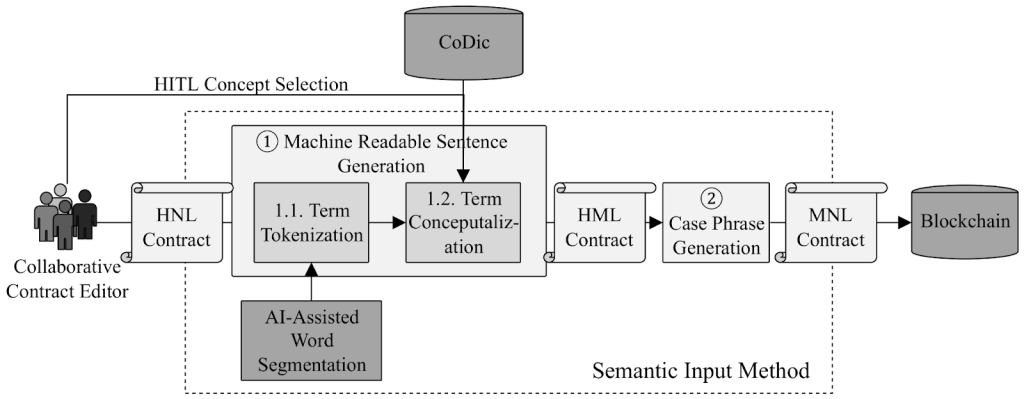
Smart Contract Generation Assisted by AI-Based Word Segmentation (Source: MDPI)
However, while an LLM like GPT-4 can generate syntactically correct and coherent smart contract code, it doesn’t truly understand the business intent or security implications behind that code. The AI predicts likely code patterns based on its training data, which may include both best practices and faulty examples. It might not know, for instance, why a certain function needs an access control modifier, or what subtle reentrancy guard is necessary in a particular DeFi context. As a result, machine-generated contracts can introduce mistakes or omissions that a human developer might catch through experience. Relying solely on AI for smart contract development can be risky—without thorough review, you could deploy a contract that works on the surface but harbors critical vulnerabilities underneath.
Hidden Risks in Machine-Generated Code
AI-generated smart contracts increase the risk of hidden logic exploits. Even if the code compiles and runs, there may be subtle flaws that malicious actors can exploit. Some common vulnerability scenarios include:
- Undetected Security Vulnerabilities: The AI might produce code with known weakness patterns—such as reentrancy opportunities, unchecked external calls, or arithmetic overflow bugs—especially if the prompt or training data didn’t emphasize secure coding. For example, an AI could omit a revert check after an external call, leaving the contract open to reentrancy attacks even though the logic otherwise looks sound.
- Logic Flaws and Misaligned Intent: Because an AI doesn’t inherently understand the purpose of the contract, it might implement logic that technically fulfills the prompt but not the real intent. Imagine a token contract where the AI accidentally leaves out a condition in the transfer function (e.g. failing to update a critical accounting variable). The contract functions in tests, but under certain conditions an attacker could exploit this logic gap to siphon funds or bypass rules. These mistakes are not syntax errors—they’re semantic bugs hidden in the business logic.
- Incomplete Access Controls: Smart contracts often require strict role-based permissions (for owners, admins, users, etc.). An AI-generated contract might miss some access control on sensitive functions. This could lead to scenarios where anyone can call administrative functions that should be restricted, creating a backdoor for exploits or governance attacks.
- Outdated Patterns: AI models train on vast code data from the past. If a model learned from older Solidity code, it might use outdated or deprecated design patterns. For instance, it might use tx.origin for authorization or not use recommended guard checks—practices that modern security standards have since warned against. These outdated patterns can introduce weaknesses that sophisticated hackers recognize even if the contract appears “normal” at first glance.
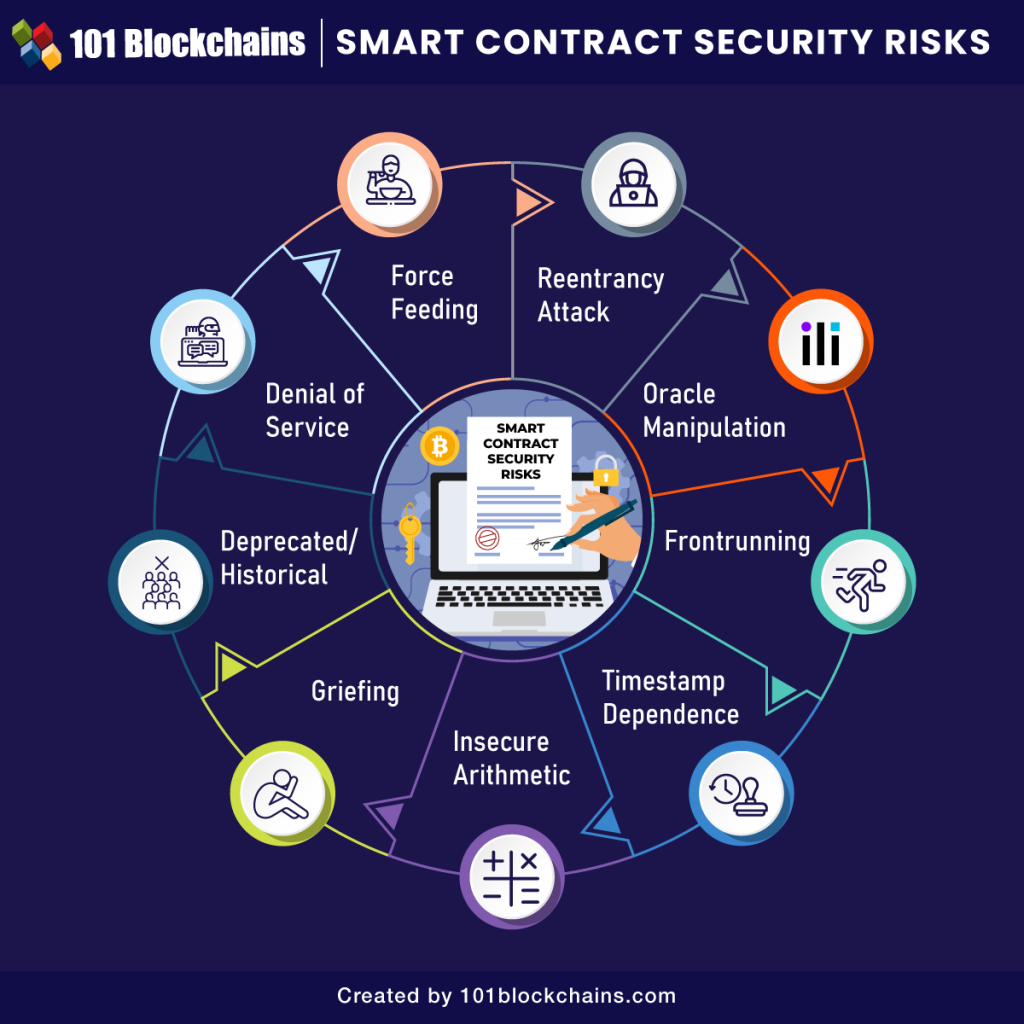
Common security risks in AI-generated smart contracts, including logic flaws, access control issues and outdated patterns that attackers can exploit (Source: 101Blockchains)
Real-world research has underscored these risks. In one study, hundreds of smart contracts generated by state-of-the-art AI models were put through security analysis tools, and many were found to have critical vulnerabilities. In another experiment, a team of researchers built an AI agent that could autonomously scan a deployed smart contract, identify a flaw, write an exploit, and execute an attack within minutes. Notably, this AI-driven agent managed to find vulnerabilities even in contracts that had passed human audits – highlighting that some issues are so hidden or complex that they slip past traditional reviews.
These examples serve as a wake-up call: AI can create new vulnerabilities just as quickly as it can code, and attackers are beginning to use AI to find those flaws. We need robust auditing and verification processes tailored for the era of AI-written code.
Why AI Smart Contract Audits Are Essential
Given the above risks, AI smart contract audits are no longer optional – they’re essential. An AI smart contract audit means a thorough security review of a contract that was created or assisted by AI, with the aim of catching vulnerabilities or logic errors that automated generation might introduce.
Here’s why these audits are so important:
- Safety of Funds and Data: Smart contracts often handle valuable assets (like cryptocurrency, tokens, or sensitive data). Any hidden bug or exploit could lead to loss of funds or unauthorized access. When code is machine-generated, the uncertainty around its correctness is higher, so an audit acts as a safety net to protect your stakeholders from potentially catastrophic losses.
- Trust and Transparency: Investors and users need confidence that a blockchain application is secure. Announcing that your contracts have undergone an independent audit (especially if code was AI-generated) greatly enhances credibility. It shows proactive risk management. In the eyes of exchange listing committees or enterprise partners, audited smart contracts (with formal reports) demonstrate that you take security seriously, which is vital for business partnerships and regulatory compliance.
- Catching What AI Missed: AI is powerful, but as mentioned, it lacks understanding of intent and context. A specialized audit can catch not just low-level bugs, but also high-level logic issues. Auditors will manually inspect the code, run tests, and consider edge cases that an AI might not anticipate. They can also compare the code to the intended functionality described by the development team, ensuring nothing got “lost in translation” from spec to code.
- Adapting to New Threats: The security landscape is always evolving. As AI tools emerge, so do new types of exploits. Regular audits (and re-audits after updates) help teams stay ahead of emerging threats. For instance, if a new kind of attack or vulnerability becomes known in the community, an audit can specifically check that your AI-generated code isn’t susceptible to that pattern. Essentially, audits provide continuous assurance, especially important when using novel development methods like LLMs that might introduce novel bugs.

Smart contract audit workflow combining automated scans and human verification to ensure AI-generated code integrity (Source: EMURGO)
In summary, AI smart contract audits ensure that the convenience of AI-generated code doesn’t come at the cost of security. They combine automated scans and human expertise to verify that your on-chain logic is not only error-free, but also aligned with your project’s intention and robust against attacks. Next, we’ll discuss how these audits are performed and what modern techniques are involved in verifying AI-written contracts.
New Approaches for Audit Automation and Logic Verification
Traditional smart contract audits involved manual code review and using static analysis tools. While those remain fundamental, auditing machine-generated contracts calls for augmented techniques. The good news is that the same AI revolution powering code generation is also delivering tools to improve audits.
Here are some modern approaches for audit automation and logic verification that organizations are adopting to secure AI-powered contracts:
- Automated Static Analysis Tools: Advanced static analyzers (e.g. Slither, Mythril, and others) can quickly scan AI-written code for known vulnerability patterns. These tools examine the contract’s source code or bytecode without executing it, flagging issues like reentrancy possibilities, unsafe math operations, or insecure use of randomness. Audit automation with static analysis is fast and can handle the scale of AI code generation (which might churn out many variants). It’s a first line of defense to catch obvious bugs that an AI might inadvertently include.
- Dynamic Analysis and Fuzz Testing: To uncover deeper logic issues, auditors use dynamic analysis techniques such as fuzzing. Fuzz testing involves running the contract in a controlled environment (or simulation) and sending a wide range of randomized inputs and transactions to it, trying to force edge-case behaviors. Modern fuzzers and symbolic execution engines (like Echidna or Manticore) can simulate complex interaction sequences. This is vital for logic verification – confirming that the contract behaves correctly under unexpected or adversarial conditions. If an AI-generated contract has an unusual logic quirk (say, it only fails when two specific functions are called in succession under certain conditions), fuzzing can often reveal that scenario.
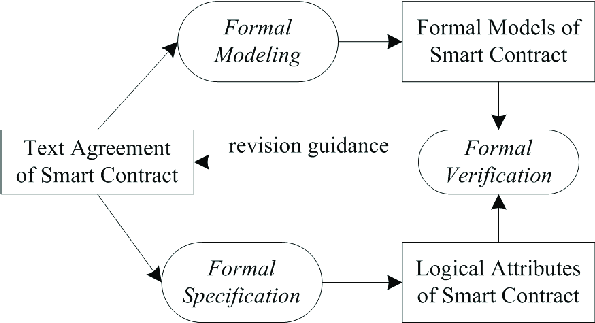
Formal verification framework illustrating how automated analysis, fuzz testing, and logic verification work together to secure AI-generated smart contracts (Source: ResearchGate)
- Formal Verification of Critical Logic: For high-stakes contracts (managing large financial values or governance controls), teams are turning to formal verification. This method mathematically proves that a smart contract’s code satisfies a given specification or invariant. Tools and frameworks can model the contract’s behavior and exhaustively verify properties. Formal verification is the ultimate logic verification technique. It’s especially useful if an AI wrote the code, because you’re not 100% sure the logic matches what you envisioned. By formally stating what the contract should do, you can check that the AI didn’t introduce any behavior outside that scope. While formal methods can be time-consuming, they bring a level of assurance that goes beyond typical testing.
- AI-Powered Audit Tools: Interestingly, AI itself is being used to audit AI-generated contracts. Researchers and security firms have developed AI-driven scanners that learn from past vulnerabilities to identify risky patterns in new contracts. For example, machine learning models (including large language models fine-tuned for security) can analyze code and pinpoint sections that “look different” from usual safe practices. Some AI audit tools rank potential issues by severity, helping human auditors focus on the most critical areas first. These AI tools excel at pattern recognition across thousands of contracts, so they can quickly spot if your AI-written code is eerily similar to a known vulnerable contract on GitHub, for instance. This audit automation augments human effort – it’s like having a tireless junior auditor that highlights suspicious parts for the senior experts to review in depth.
- Continuous Monitoring and On-Chain Checks: Auditing doesn’t stop at deployment. With the rise of on-chain AI and automation, projects are starting to implement continuous security monitoring. This can include on-chain watchers (sometimes powered by AI) that monitor transactions and contract state in real time for anomalies. For instance, an AI agent could be tasked with watching a deployed smart contract for any irregular patterns (sudden large withdrawals, sequences of calls that match known attack patterns, etc.) and alert the team or even pause the contract via a circuit breaker if something looks very wrong. While this drifts into operational security more than auditing, it’s part of a holistic approach. If AI-generated logic somehow slipped a flaw into production, early detection by on-chain AI governance mechanisms can minimize damage. In essence, defensive AI can counteract offensive AI. Forward-looking organizations are researching on-chain AI governance – systems where AI helps enforce rules and respond to incidents automatically on the blockchain.
All these approaches reinforce each other. A thorough audit of an AI-generated smart contract might use multiple layers: static analysis to get quick coverage, AI-powered scanners for pattern matching, manual code review to understand intent, dynamic testing to probe for weaknesses, and possibly formal verification for the most mission-critical components. By combining these, you significantly reduce the chance that any bug (especially those lurking in logic or edge cases) goes unnoticed.
Conclusion
AI is transforming how we build technology, and AI-powered smart contracts are a prime example of this revolution. Speed, efficiency, and creativity in code generation are reaching new heights thanks to LLMs and automated tools. Yet, as we’ve discussed, this leap forward comes with new responsibilities. Security and trust cannot be taken for granted when machine-generated code runs our digital agreements. Auditing machine-generated on-chain logic is not just a technical formality, but a business imperative – it’s about safeguarding assets, users, and reputations in the blockchain ecosystem.
The path forward is clear: we must pair the power of AI with rigorous verification. By investing in AI smart contract audits, leveraging audit automation technologies, and insisting on thorough logic verification, organizations can confidently embrace AI in development without leaving their projects exposed. It’s about striking the balance between innovation and caution. With the right processes, AI-written smart contracts can be just as secure (or even more so) as those hand-coded from scratch, because we can apply equally advanced AI in testing and safeguarding them.
At the end of the day, building trust in AI-generated code will differentiate the leaders in the blockchain space. Stakeholders from CTOs to investors will sleep better knowing that every smart contract, whether crafted by a human, an AI, or both, has been audited and proven secure.
As you explore the advantages of AI in your development workflow, make sure you have a partner who understands how to secure it. Twendee’s blockchain and AI experts are here to help you audit, verify and fortify your smart contracts against hidden risks. Don’t let a hidden bug or exploit undermine your innovation.
Contact Twendee today to learn how our IT services and security solutions can safeguard your AI-powered smart contracts and empower your business with confidence in the digital economy.
Contact us: Twitter & LinkedIn Page
Read latest blog: E-wallet app development cost estimates for 2025





