Web3 development cost is rarely “just engineering hours.” It is the sum of on-chain risk, infrastructure exposure and operational maturity across months or years. Many Web3 platforms go over budget for one predictable reason: early estimates focus on shipping features, while the real spend accumulates in smart contract security, blockchain infrastructure cost and web3 maintenance cost after launch.
A practical benchmark shows how wide the spread can be. Depending on scope and architecture, a Web3 build can range from an MVP-level build to enterprise-grade systems that cost multiples more, because complexity and security scale non-linearly (PixelPlex)
This article breaks down the Key Cost Factors in Web3 Development and Maintenance in a way that supports CEO and CTO planning, developer execution and investor due diligence, with cost items that are frequently underestimated.
Key Cost Factors in Web3 Development and Maintenance
1. Smart contract development cost is not coding, it is irreversible design
Smart contracts are closer to “financial logic with permanent consequences” than typical application code. That is why smart contract development cost grows fastest when the system includes value custody, liquidation logic, pricing curves, cross-chain messaging, or governance.
What usually gets underestimated is not the initial build, but the extra engineering required to make the contract safe to upgrade, observable in production and constrained under worst-case scenarios.
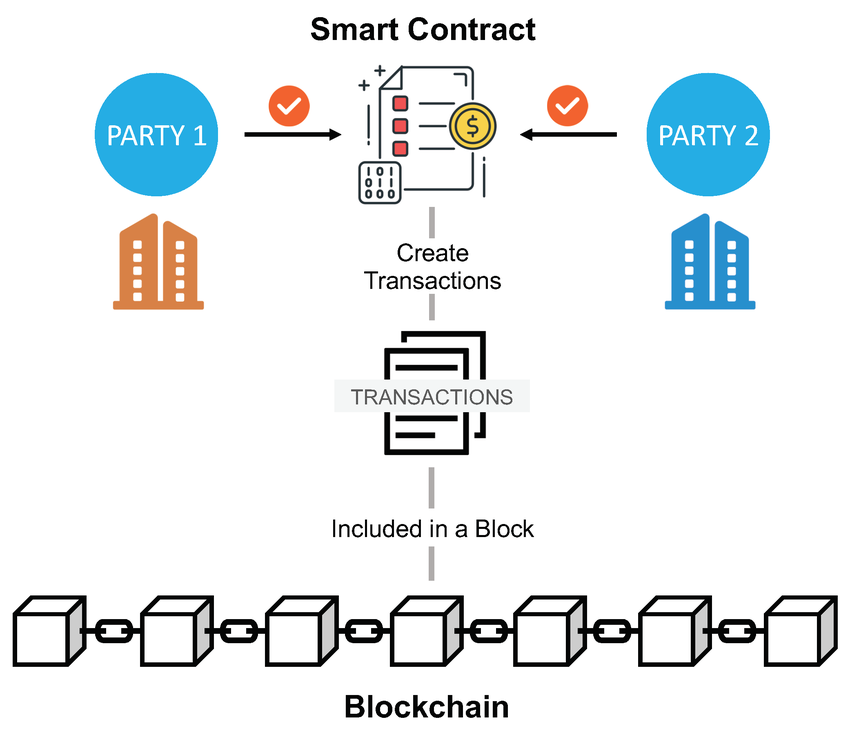
Smart contracts automate transactions between parties and permanently record execution logic on the blockchain, making design errors costly and irreversible (Source: researchgate)
Cost drivers that expand smart contract development cost:
- Complexity of state and invariants: more storage, more edge cases, more test vectors.
- Protocol integrations: DEX routing, lending protocols, bridges, oracle networks.
- Upgrade strategy: proxy patterns, migration paths, backward compatibility.
- Formal testing depth: property-based tests, fuzzing, differential tests.
Security-focused Web3 builders commonly cite audit-related ranges that reflect how quickly “complex logic” increases cost: basic audits around $10k–$20k, complex DeFi audits often $20k–$50k+ and advanced systems can exceed that. (ULAM LABS+1)
This matters because smart contract development is inseparable from security work. In cost planning, the contract budget should be treated as: build + test + audit prep + post-audit remediation + re-audit for changes (not just “write Solidity”).
2. Blockchain infrastructure cost is usage-based and volatility-sensitive
In Web2, infrastructure cost is often predictable with capacity planning. In Web3, blockchain infrastructure cost is tied to:
- Transaction throughput and chain conditions (gas volatility)
- Read workload (RPC calls, indexing, analytics)
- Multi-chain scope and redundancy requirements
- Data retention and archival needs
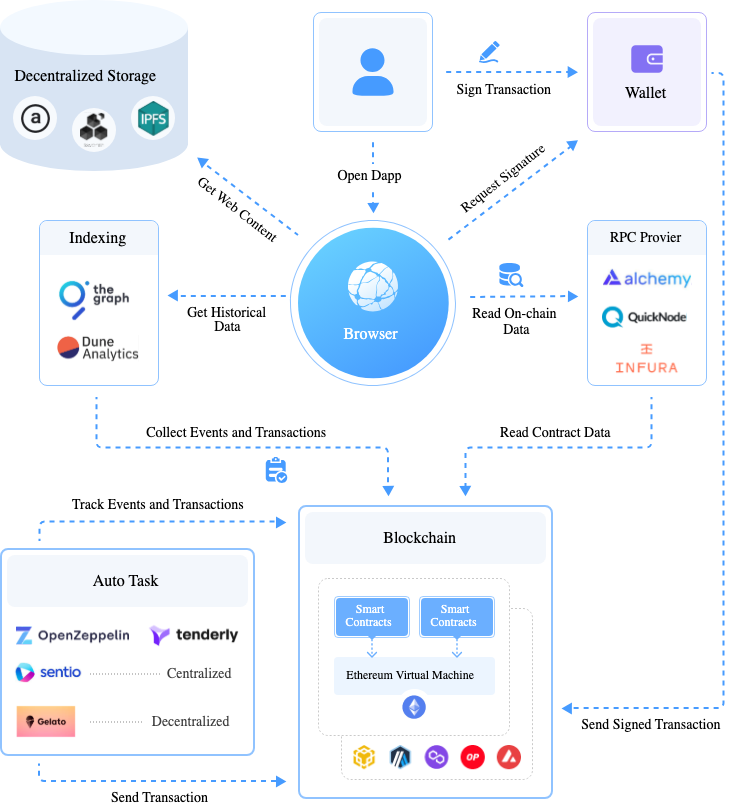
Web3 application infrastructure relies on multiple usage-based components including RPC providers, indexing services, decentralized storage, and automation layers, causing infrastructure costs to scale with on-chain activity rather than fixed capacity (Source: 57blocks)
Underestimated infrastructure line items
- RPC provider subscription (for reliability and throughput): Infura’s public pricing shows paid tiers starting at $50/month and scaling upward with throughput needs (Infura+1)
- Operational redundancy: production platforms often pay for multiple providers to mitigate provider outages and rate limits.
- Indexing and data services: subgraphs, event indexing, analytics pipelines (often a persistent monthly cost).
- Gas strategy: deployment and upgrades can be expensive on L1 during congestion; deployment costs can become material at scale.
Why this cost surprises teams:
- A usage spike is not only “more users.” It is more reads, more signature checks, more events indexed, more retries during congestion.
- Chain choice is an economic decision. L2s can reduce costs for users, but multi-chain support multiplies integration and monitoring effort.
3) Security cost is a recurring operating expense, not a one-time gate
Most budget models treat audits as a checkbox before launch. Mature models treat security as an ongoing cost center. Audit costs and why they escalate:
- Market ranges commonly cited for audits (USD) reflect complexity: basic contract audits $10k–$20k, complex dApps/DeFi $20k–$50k, and larger ecosystems higher (ULAM LABS+1)
- Post-audit changes often require re-audit because the threat model changes with every meaningful modification (23studio)
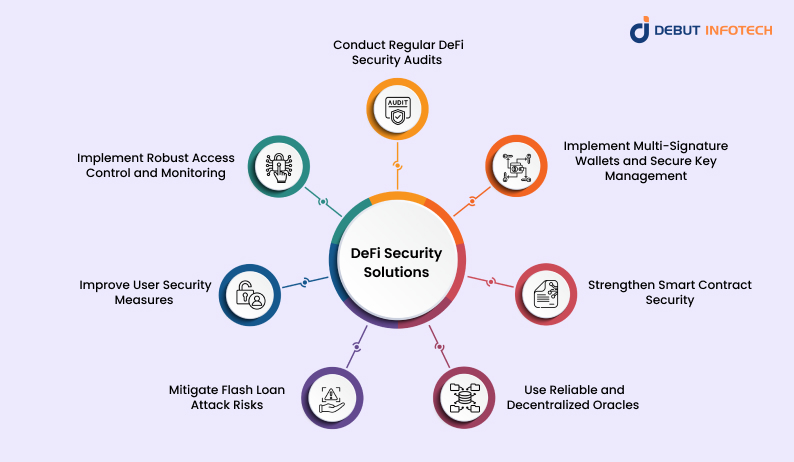
DeFi security requires continuous operational investment across audits, access control, monitoring, key management, and oracle reliability, making security a recurring cost center rather than a one-time pre-launch activity (Source: Debut Infotech)
Security spend that is often missed:
- Threat modeling workshops before implementation
- Audit readiness: documentation, test coverage, invariants, deployment scripts
- Bug bounty program and triage process
- Monitoring: anomaly detection, exploit signals, admin key activity alerts
For investors, a budget that includes only a single audit line item is often a risk signal, not a cost saving.
4. Web3 maintenance cost is where total cost of ownership is won or lost
Web3 maintenance cost should be treated as a real budget line from day one. A common guideline used in software budgeting is that annual maintenance can range around 15%–25% of the initial development cost, depending on complexity and operational maturity (LtsGroup+1)
In Web3, maintenance is not only bug fixes. It includes:
- Protocol and wallet compatibility changes (wallet standards, provider changes)
- Dependency updates (SDKs, libraries, contract tooling)
- Security patch process (incident response readiness)
- Infrastructure tuning (RPC throughput, indexing performance, cost optimization)
- Governance operations if token-based governance exists
Maintenance is underestimated because it is not “new features,” yet it determines platform reliability, user trust and incident resilience.
Conclusion
The platforms that survive are rarely the ones that “spent the most.” They are the ones that treated web3 development cost as a strategic design variable, budgeting realistically for smart contract development cost, blockchain infrastructure cost, and web3 maintenance cost before launch pressure sets the architecture in stone.
Twendee supports organizations in turning Web3 from an uncertain build into an engineered plan with measurable cost controls. The practical difference is front-loading decisions that prevent the most common overruns:
- Technical architecture and cost model from day one: on-chain/off-chain split, chain strategy, security scope, infrastructure plan.
- Smart contract delivery with security built in: testing depth, audit readiness, remediation workflow.
- Operational planning for web3 maintenance cost: monitoring, upgrade processes, incident playbooks, and cost optimization for RPC and indexing.
If a Web3 platform needs a clear technical roadmap, realistic budget model and production-grade delivery, Twendee can help define architecture, security scope and maintenance planning end-to-end.
Contact us: Twitter & LinkedIn Page
Read latest blog: New 2025 Cost Breakdown of Building a Multi-Chain Web3 Product





