The convergence of artificial intelligence and blockchain is redefining how smart contracts make decisions. In this new paradigm often termed AI agents blockchain integration, autonomous AI-driven programs operate on blockchain networks to enhance and automate decision-making.
Unlike traditional smart contracts with static logic, these AI agents bring dynamic intelligence, an “upgrade” that allows contracts to adapt, learn and act independently based on real-time data. Tech leaders and investors are taking note: billions of dollars are flowing into this space, with on-chain AI agent activity surging by 86% in 2025 alone. Clearly, AI agents on blockchain are more than a buzzword; they’re becoming a pivotal innovation for the future of decentralized technology.
What Are AI Agents on Blockchain?
AI agents on blockchain are autonomous software entities that observe their environment, make decisions, and act independently to achieve specific goals without human intervention. Think of them as intelligent bots or digital assistants that can handle tasks on your behalf.
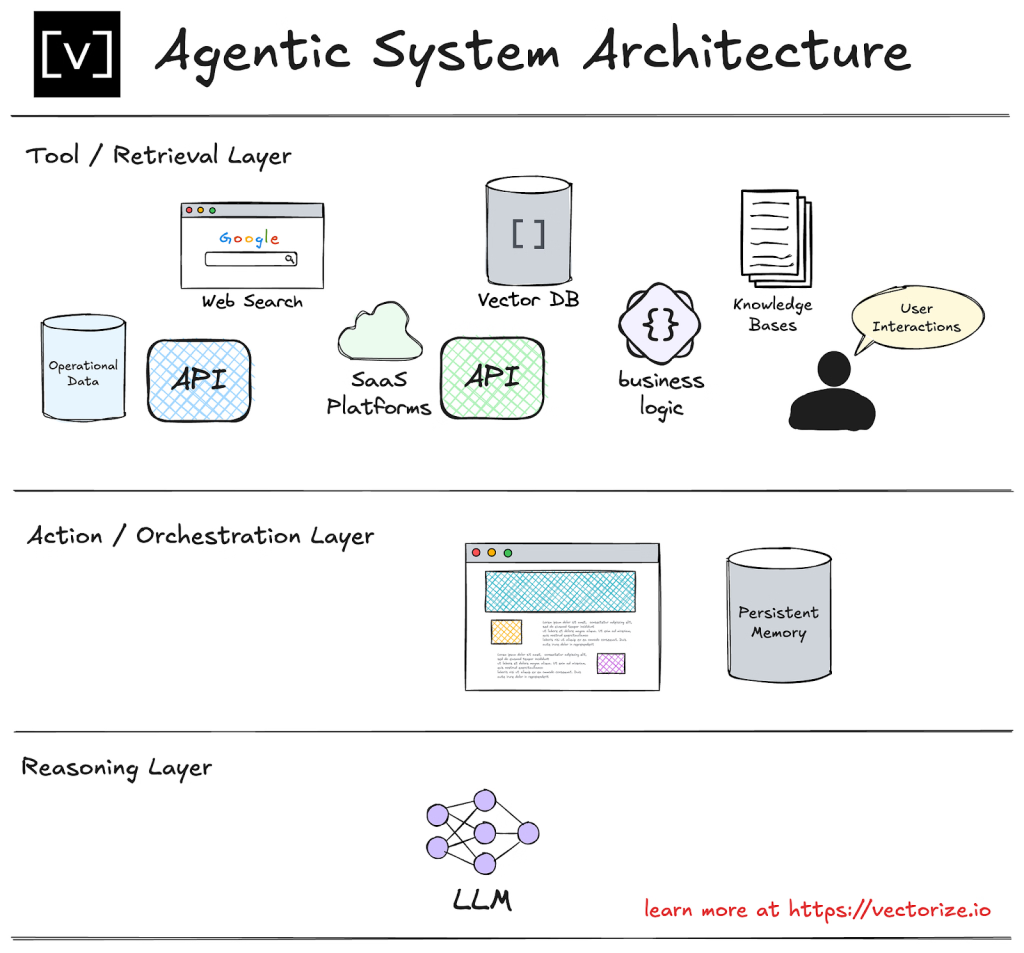
Agentic system architecture: tool/retrieval layer → reasoning (LLMs) → action / orchestration layer (Source: vectorize)
What sets blockchain-based AI agents apart from regular AI applications is that they are deeply integrated into decentralized systems. They can execute smart contract logic, perform blockchain transactions, interact with decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, and automate complex workflows without constant supervision.
Key characteristics of blockchain AI agents include:
- Trustless Execution: Every action and decision is enforced by smart contracts, ensuring predictable behavior and tamper-proof outcomes. The blockchain provides a secure execution environment for the agent’s logic.
- Secure Asset Management: AI agents can hold crypto wallets, sign transactions, and manage tokenized assets directly on-chain. This means an agent could, for example, autonomously move funds or rebalance a portfolio under predefined rules.
- Transparent Audit Trail: Because every agent action is recorded on the blockchain, all decisions and changes are fully traceable and transparent. Stakeholders can audit the agent’s behavior in real-time, which is crucial for trust in automated decisions.
In essence, an AI agent on blockchain can be viewed as a smart contract with a brain. It combines the self-executing reliability of smart contracts with the adaptive decision-making of AI. For instance, imagine an AI acting as a DAO’s treasurer that autonomously manages budgets and approves payments according to governance rules. Or picture an AI trading bot that 24/7 scans on-chain data and off-chain news to execute trades at optimal times.
These examples are not science fiction, they reflect real prototypes of AI agents handling tasks like portfolio rebalancing and treasury management entirely on-chain.
How AI Agents Redefine Smart Contract Logic
Traditional smart contracts operate on hard-coded logic, they follow static “if-this-then-that” rules defined at deployment. This rigidity means ordinary contracts can’t easily adapt to new information or complex scenarios beyond their programming.
AI agents are changing that paradigm by introducing adaptability and intelligence into contract behavior. In fact, smart contracts augmented with AI can move beyond simple rules and make nuanced decisions based on data analysis and learned experience.
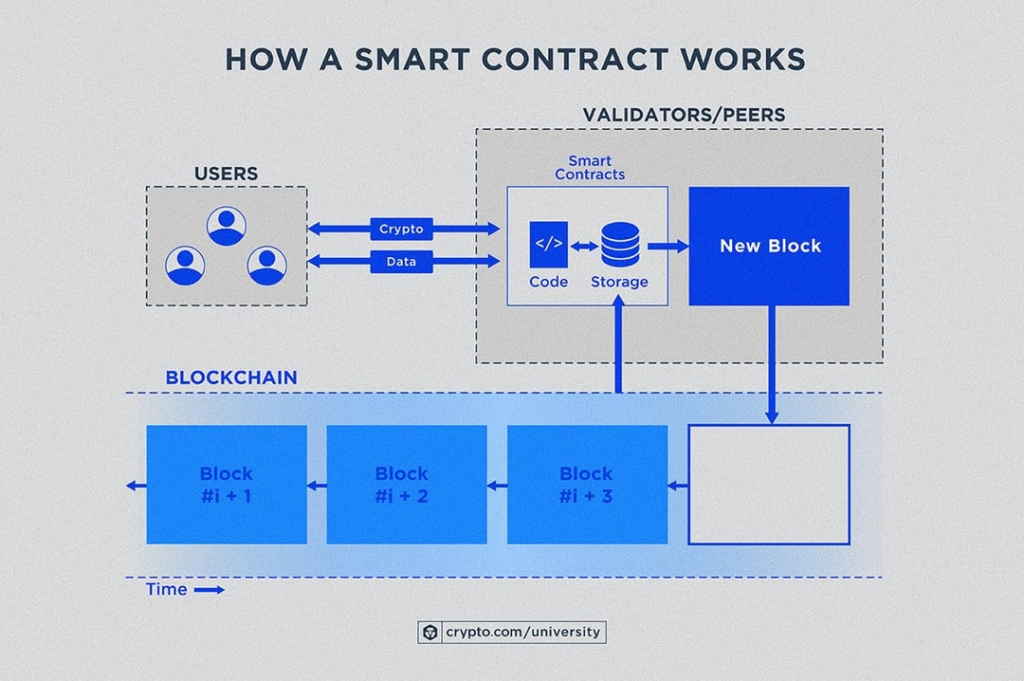
Diagram explaining how a smart contract works: transaction flow, block validation, storage, and execution (Source: Crypto)
Key ways AI agents redefine smart contract decision-making include:
- Dynamic Decision-Making: AI agents enable smart contracts to analyze diverse data (market conditions, user behavior, sensor inputs, etc.) and respond in real time. Instead of a fixed threshold or condition, the contract’s actions can vary based on what the AI learns. This makes outcomes more accurate and context-aware – a major evolution from one-size-fits-all logic.
- Smart Contract Automation: Integrating AI agents leads to a new level of smart contract automation. These agents continuously monitor conditions and trigger contract functions on their own. They can execute transactions, adjust parameters, or launch sub-contracts proactively when certain patterns in data are recognized. This autonomous decision capability means contracts don’t have to wait for human inputs to react. For businesses, this translates to hands-off operations – agreements that self-optimize and manage themselves according to high-level goals.
- Proactive Optimization: An AI-enhanced contract can optimize outcomes by anticipating events. In a decentralized energy grid scenario, an AI agent could predict demand spikes and automatically adjust pricing or energy distribution to maintain efficiency. Similarly, in finance, an AI-driven smart contract might adjust interest rates or collateral requirements on the fly based on risk predictions, something static code could never do. This kind of proactive tuning keeps systems efficient and resilient without manual oversight.
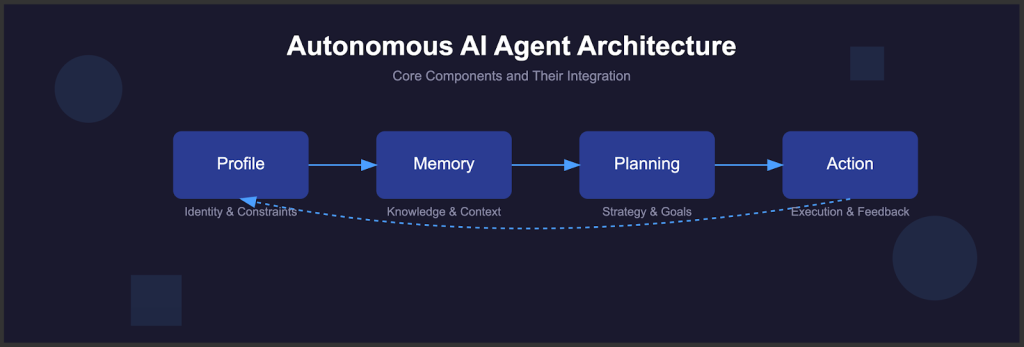
Diagram of autonomous AI agent: memory, planning, decision loops (Source: guptadeepak)
- Personalization and Adaptability: AI agents can tailor smart contract behavior to specific user needs or evolving business policies. By learning from historical data and preferences, an AI agent might adjust contract terms (within allowed bounds) to better fit a situation. For instance, a lending smart contract could personalize loan terms or collateral levels for users based on their credit behavior as assessed by an AI. This adaptability makes contracts far more flexible and business-friendly, essentially evolving alongside your organization.
- Streamlined Complex Decisions: AI can also help in areas where rule-based contracts struggle, such as dispute resolution or ambiguous scenarios. If a contractual outcome is unclear (say, whether a service level agreement was truly met), an AI agent can analyze logs, communications, and performance data to suggest a fair decision. This assists in resolving issues faster and with more data-backed objectivity, reducing the need for lengthy human arbitration.
In summary, AI agents transform smart contracts from static code to intelligent actors. By blending AI’s learning and decision-making prowess with blockchain’s reliability, we get contracts that don’t just execute instructions, but can figure out which instructions to execute for optimal results. This evolution in logic is redefining automation in sectors from finance to supply chain.
Use Cases and Impact Areas
AI agents on blockchain are making waves across various domains, driving both efficiency and innovation. Below are key areas where AI-driven smart contracts are delivering value:
- Autonomous DeFi Strategies (DeFi AI): In decentralized finance, AI agents are automating complex strategies that were once the realm of expert traders. They can analyze real-time market data, execute trades at the perfect moment, and continuously rebalance portfolios to maximize yield. These autonomous DeFi bots improve returns and manage risk (assessing factors like APY, gas fees, impermanent loss) without needing a human in the loop. This level of smart contract automation in trading and yield farming allows even regular users to benefit from sophisticated financial strategies.
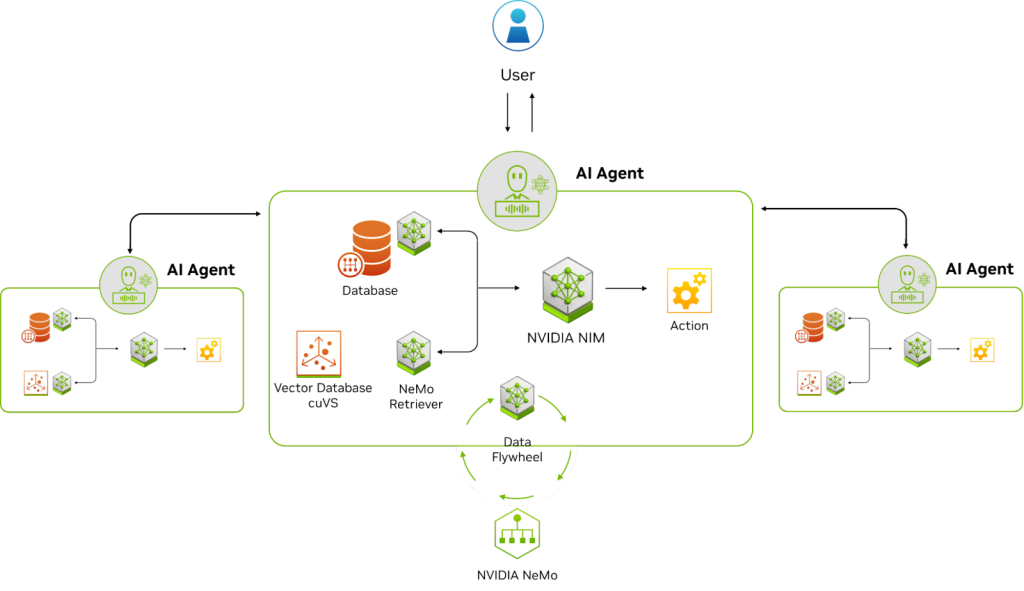
Flow of AI agent interacting with data sources & external tools, with memory and action components (Source: NVIDIA)
- AI-Powered Smart Contract Governance: Managing decentralized organizations (DAOs) and protocols can be complex, but AI agents are stepping in to enhance governance. AI governance tools can digest and analyze governance proposals, financial statements and community sentiment much faster than any human team. In practice, an AI agent could forecast the outcomes of a DAO proposal or flag anomalies, helping stakeholders make informed votes. Furthermore, AI agents acting as autonomous treasurers can enforce budget rules – automatically approving expenses that fit policy and denying those that don’t. This brings consistency and insight to blockchain governance, as the AI provides data-driven recommendations and ensures rules are followed without bias.
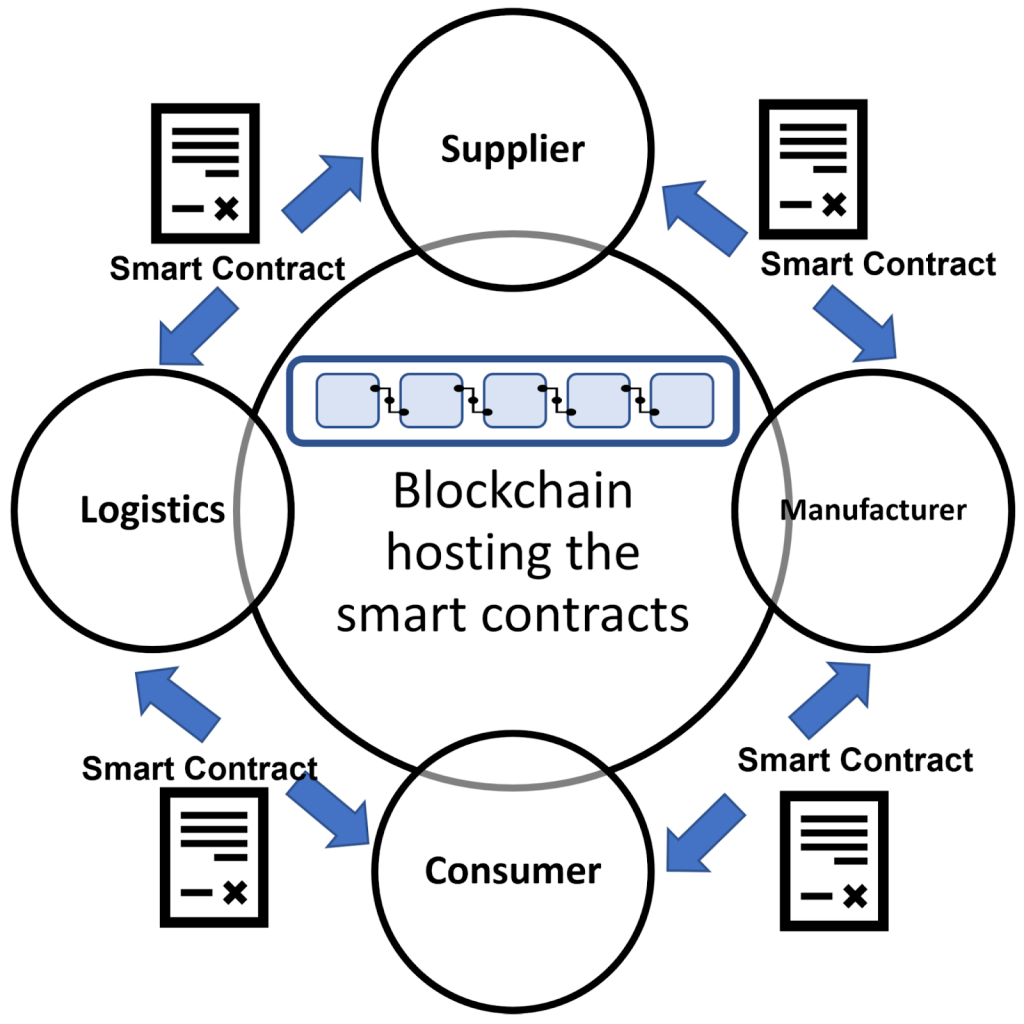
Smart contract architecture for logistics / supply chain: illustrating contracts, stakeholders, and automated triggers (Source: MDPI)
- Intelligent Supply Chain & Operations: Outside of finance, AI agents on blockchain are revolutionizing supply chain management and other operational workflows. These agents, each with their own blockchain identity, can track products, verify origins, and execute supply chain contracts (like payments release or inventory orders) automatically as conditions are met. By blending AI insights with the transparency of blockchain, companies gain autonomous decision-making in logistics reducing delays and human error. The entire process becomes more transparent and trustworthy since every step is recorded on-chain.
- Continuous Security & Risk Monitoring: Security is a critical aspect of smart contracts, and AI agents are proving invaluable here. These agents can serve as tireless auditors, constantly scanning smart contract code and transactions for vulnerabilities or anomalies. Trained on vast data of hacks and exploits, an AI security agent might detect a potential bug or a suspicious pattern (like an abnormal token transfer) and instantly alert the network or even patch the issue if authorized. This kind of AI-driven protection makes blockchain systems safer and more robust. For instance, before a flaw can be exploited in a DeFi protocol, an AI agent could identify it and initiate a fix in real-time – something impossible with periodic manual audits. The result is a more secure ecosystem, where threats are addressed proactively and automatically.
- Enhanced User Experience & Services: AI agents are also improving user interactions and services on blockchain platforms. Consider personalized AI assistants embedded in wallets or dApps, they can guide users, answer questions, or execute tasks via natural language commands. Projects like Fetch.ai have introduced wallet-native agents that can fetch data or perform routine transactions for you. In customer-facing scenarios, chatbots backed by AI can help users navigate complex DeFi products or NFT marketplaces. All of this lowers the entry barrier for new users and offers a more intuitive experience, while the underlying smart contracts still guarantee trust and enforceability.
Each of these use cases demonstrates the transformative impact of combining AI agents with blockchain. From finance (where DeFi AI creates smarter financial products) to operations (where automation and transparency are paramount), AI agents are pushing the envelope of what smart contracts can do. They not only execute decisions faster and often more accurately than humans, but also operate 24/7, bringing a level of consistency and efficiency that traditional systems can’t match.
Conclusion
AI agents on blockchain are redefining how smart contracts make decisions, transforming them from static code into intelligent systems capable of adaptive, autonomous execution. The result is smarter automation, better governance and more resilient decentralized systems.
Yet, deploying AI-driven smart contracts requires navigating complex challenges from integrating machine learning models with on-chain logic to ensuring compliance, governance, and security. This is where Twendee Labs comes in.
– We design and implement AI + blockchain integration that enables businesses to build autonomous, transparent, and secure systems.
– Our expertise covers smart contract automation, AI governance frameworks, and compliance-ready DeFi AI solutions.
– Whether you’re exploring tokenized finance, AI-driven DAOs, or real-time autonomous decisions, Twendee Labs provides the technical depth and strategic clarity to help you scale.
Now is the moment to act. Organizations that embrace AI agents blockchain solutions today will lead tomorrow’s markets in automation and trust.
Connect with us on LinkedIn or X to explore how Twendee can support your transformation: Twitter & LinkedIn Page
Read latest blog: Layer-2 Costs Are Dropping, But Enterprise Integration Is Still a Challenge





