Smart contracts were meant to make blockchain systems trustless yet they’ve become one of its biggest trust gaps. According to Hacken’s Web3 Security Report (Q1 2025), more than $2 billion was lost in just 90 days, with access control exploits and logic vulnerabilities making up the majority of financial damage. Despite countless audits and improved developer tools, vulnerabilities persist, evolving as fast as the ecosystems they inhabit.
This raises a crucial question: are today’s smart contract auditing frameworks truly keeping pace with the complexity of Web3?
Why Smart Contract Vulnerabilities Still Cost Billions
Despite improved auditing practices, Web3 remains plagued by preventable breaches. According to Hacken’s Q1 2025 Security Report, smart contract exploits alone accounted for over $2 billion in losses, with access-control errors making up nearly 80%. This persistence reveals not a lack of tools, but a mismatch between what current smart contract auditing frameworks analyze and how real-world exploits evolve.
- Cross-Contract Dependencies Evade Detection: Most auditing tools still analyze smart contracts in isolation. Yet modern Web3 systems like decentralized exchanges or lending protocols rely on inter-contract logic, where a single state change can cascade across multiple contracts. Static analysis frameworks such as Slither and Mythril efficiently catch data-flow and syntax-level issues but fail to trace cross-contract state transitions. This limitation explains how major incidents, such as the 2024 Curve pool exploit, bypassed audits despite “clean” reports. The vulnerability wasn’t a line of faulty code, but an overlooked interaction between modules that no single static tool could fully simulate.
- Economic Logic and Governance Are the New Attack Surfaces: Today’s most damaging breaches no longer depend solely on coding errors. Instead, they exploit economic and governance design flaws – areas most auditors still treat as secondary. Attackers increasingly manipulate incentive mechanisms and governance votes through flash loans or liquidity distortions, draining reserves without breaching any explicit function rules. These invisible failures of economic logic expose a new category of risk: one that auditing frameworks can’t yet quantify. Until security analysis incorporates simulation of token dynamics, voting behaviors, and incentive feedback loops, protocols will remain vulnerable even if their code compiles perfectly.
- AI Auditing Still Lacks Semantic Understanding: AI-powered frameworks have made significant progress in accelerating vulnerability discovery. Models based on large language architectures can scan thousands of lines of Solidity faster than any human auditor. Yet, most of these systems operate on pattern recognition, not comprehension. An AI might detect irregular opcodes or unreferenced variables, but it cannot always interpret intent, such as whether a function’s logic aligns with the protocol’s business rules. This is the gap where AI efficiency meets its boundary: it can point to anomalies, but not infer purpose.
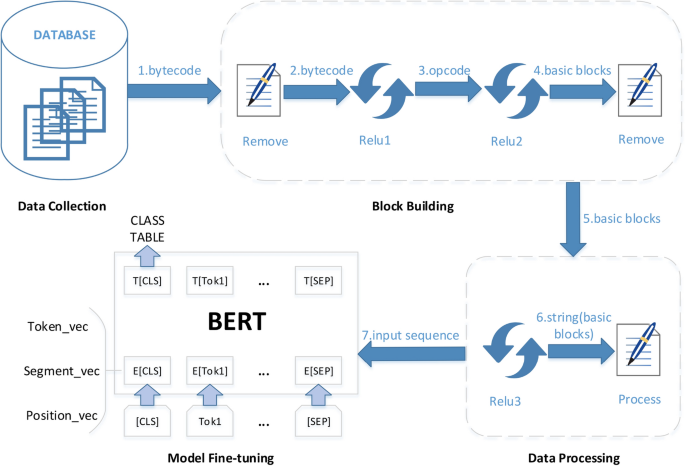
AI-based auditing model visualized through BERT bytecode analysis demonstrating automation’s reach in pattern recognition but also its current inability to infer developer intent or business logic (Source: Multimedia Systems 30, 204).
The diagram above captures how advanced AI models process bytecode to detect anomalies, but this still represents a syntactic understanding of security, not semantic assurance. Until auditing systems merge AI-driven insights with human reasoning, verification will remain partial at best.
2025’s Leading Frameworks Redefining Smart Contract Security
In 2025, smart contract auditing frameworks have evolved beyond passive code scanners into active intelligence systems. They no longer focus solely on spotting syntax errors or known exploits; instead, they model behavior, validate intent, and simulate economic risk. This evolution signals a shift from auditing as an afterthought to security as a built-in development discipline.
The frameworks setting new industry standards share three defining capabilities that separate them from the static tools of the past.
1. Hybrid Frameworks Unite Static and Symbolic Analysis
Legacy audits were fast but shallow, often limited to syntax checks and heuristic rule matching. The leading 2025 frameworks merge static analysis (detecting pattern-level errors) with symbolic execution (replaying transaction logic across countless input scenarios). Frameworks like Slither and Manticore now work in tandem—Slither’s precision in scanning Solidity and inheritance hierarchies complements Manticore’s ability to emulate smart contract state changes.
This dual-layer approach reduces false positives while uncovering cross-function and cross-contract vulnerabilities, particularly in systems like DEX pools and lending vaults. Rather than just detecting what’s “wrong” in code, these frameworks analyze why it might break in production, bridging the gap between theory and on-chain behavior.
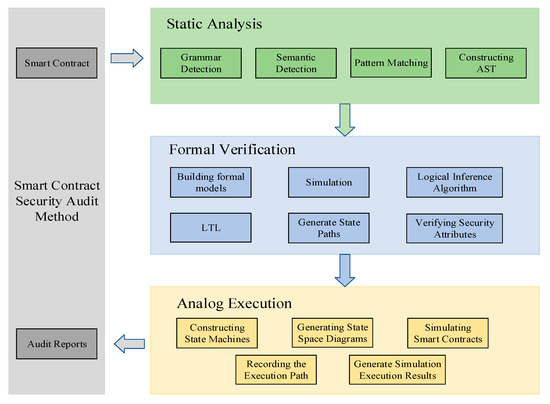
A conceptual flow showing how hybrid auditing frameworks layer static, symbolic, and analog testing to replicate blockchain execution paths and identify logic flaws missed by static scans (Source: MDPI).
2. Formal Verification Delivers Mathematical Confidence
For DeFi and DAO systems managing billions in on-chain value, “probably secure” is no longer enough. The most advanced auditing frameworks now integrate formal verification, transforming code auditing into a mathematical proof of correctness. By modeling contract properties as logical formulas, frameworks like Mythril, Echidna, and Certora Prover ensure that critical operations, from collateral liquidation to governance voting, behave exactly as intended under all possible states.
This approach changes the nature of blockchain assurance. Instead of trusting an auditor’s interpretation, teams can rely on provable invariants: mathematical guarantees that a given exploit path simply cannot exist. For protocols dealing with composable assets and recursive lending, this precision defines the new threshold of “secure.”
3. AI-Assisted Auditing Adds Contextual Intelligence
The third frontier is AI-augmented analysis, where automation gains context. Machine learning models, trained on vast exploit datasets, can now infer vulnerability patterns that resemble intent deviations – code that technically works but violates functional goals. Transformer-based frameworks built on architectures like BERT treat bytecode as language, learning to identify unusual semantic relationships between contract components.
These models not only flag potential issues but rank them by impact, differentiating between trivial code smells and catastrophic access-control risks. They give human auditors an intelligent baseline, accelerating manual verification without replacing it. The result is faster, deeper, and more adaptive auditing pipelines built for continuous learning.
This convergence between automated intelligence and human accountability mirrors broader trends across decentralized infrastructure. A deeper discussion can be found in this analysis, exploring how AI agents reshape accountability in blockchain ecosystems.
Building Trust Through Hybrid Intelligence
Automation has become the cornerstone of modern auditing — yet trust in blockchain security still depends on how well human judgment and AI precision work together. Machine learning can scan thousands of contracts in minutes, flagging potential exploits such as reentrancy or overflow, but no algorithm fully grasps economic intent, governance logic, or risk prioritization. That’s where human insight remains indispensable.
The most advanced smart contract auditing frameworks in 2025 thrive on this synergy:
- AI accelerates detection by identifying vulnerabilities and anomaly patterns far beyond human speed.
- Human auditors interpret context, evaluating whether those findings threaten actual user assets or operational integrity.
This balanced interplay turns audits from static checklists into dynamic assurance systems, capable of adapting to evolving codebases and attack vectors.
Twendee Labs applies this hybrid approach by combining AI-driven static analysis with manual verification from domain experts. Its process ensures that every flagged risk is interpreted within the broader business logic, essential for complex ecosystems such as DeFi and cross-chain applications. This not only prevents false positives but also strengthens confidence in protocol sustainability and investor safety.
Another defining evolution is continuous auditing. Modern security doesn’t end after deployment. Twendee Labs embeds automated re-testing within CI/CD pipelines, enabling teams to monitor, validate, and respond to risks in real time. Through this integration, audit quality becomes a continuous cycle of improvement rather than a one-time milestone.
Ultimately, hybrid intelligence isn’t about replacing humans with machines but amplifying their strengths. The next generation of auditing frameworks will belong to those who align automation’s scale with human understanding, achieving both precision and purpose in Web3 security.
Twendee Labs’ AI-first audit workflow bridges automation and human expertise to deliver practical, resilient blockchain security outcomes. (Source: Twendee Labs)
Conclusion
Smart contract security is no longer about finding bugs, it’s about building systems that learn, adapt, and safeguard value over time. Post-2025, the frameworks that unite automation, formal verification, and human reasoning will define blockchain trust itself.
Discover how Twendee Labs helps teams strengthen audit reliability through AI-assisted verification and continuous monitoring. Stay connected via LinkedIn and X for more insights on next-generation blockchain security.





